In modern healthcare, the quest for effective solutions to promote healing and minimize complications has led to remarkable advancements in medical technology. One such innovation is the triple-layer membrane, a sophisticated structure designed to enhance tissue repair while providing superior protection against infections. This article delves into how triple-layer membranes work, their benefits, and their applications in healthcare, focusing on their role in accelerating healing and reducing infection risks.
What is a Triple Layer Membrane?
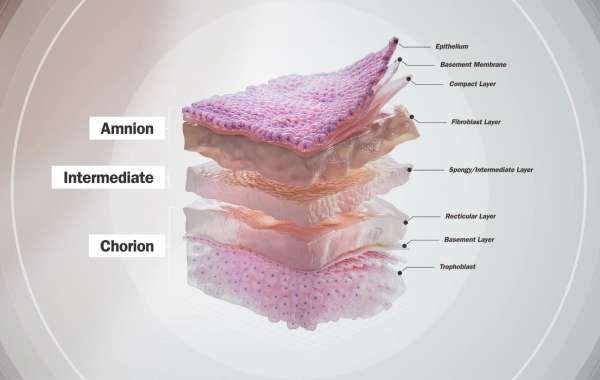
A triple-layer membrane consists of three distinct layers, each engineered to fulfill specific functions that collectively promote effective healing. The outermost layer acts as a protective barrier, shielding the wound or surgical site from external contaminants. The middle layer provides bioactive components that stimulate tissue regeneration, while the innermost layer serves as a scaffold that supports cellular growth and integration.
This multi-layer design allows triple-layer membranes to address various challenges in wound healing, making them a versatile tool in both surgical and non-surgical settings.
1. Accelerating Healing Processes
One of the primary advantages of triple-layer membranes is their ability to accelerate the healing process. The combination of protective, bioactive, and scaffold layers creates an optimal environment for healing.
Outer Layer Protection
The outer layer of the membrane serves as a shield against bacteria, dirt, and other harmful agents. By preventing contamination, this layer reduces the risk of infections, which can delay healing and lead to complications. The membrane's breathable nature allows for moisture control while still offering robust protection.
Middle Layer Bioactivity
The middle layer is infused with bioactive materials, such as growth factors and collagen, which promote cellular activities essential for healing. These components stimulate cell proliferation and migration, encouraging the growth of new tissue. The presence of these growth factors accelerates the natural healing processes, leading to faster recovery times.
Inner Layer Scaffold
The innermost layer provides a three-dimensional scaffold that supports cell attachment and organization. This scaffold structure mimics the natural extracellular matrix, allowing cells to grow and regenerate in a conducive environment. The scaffold promotes tissue integration, ensuring that newly formed tissue aligns well with surrounding areas, which is crucial for overall healing and functionality.
Clinical Application:
In surgical settings, such as orthopedic procedures or skin grafts, the application of triple layer membranes has shown to significantly shorten recovery times. Patients experience improved healing outcomes, allowing them to return to normal activities sooner.
2. Minimizing Infection Risks
Infection is a common and serious complication in wound healing. Triple-layer membranes play a vital role in minimizing this risk through their innovative design.
Barrier Protection
The outer layer of the membrane creates a physical barrier that prevents pathogens from entering the wound site. This barrier is critical in keeping bacteria and other harmful agents at bay, especially in high-risk environments like hospitals where the risk of infection is elevated.
Antimicrobial Properties
Many triple-layer membranes incorporate antimicrobial agents within their structure. These agents actively combat bacteria and reduce the likelihood of infection. By integrating these properties directly into the membrane, healthcare providers can ensure that patients receive continuous protection throughout the healing process.
Moisture Management
Proper moisture balance is essential for effective wound healing. Excess moisture can lead to maceration and increase infection risks, while inadequate moisture can hinder the healing process. The design of triple layer membranes allows for optimal moisture management, keeping the wound environment conducive to healing while minimizing the risk of infection.
Clinical Application:
In cases of chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers or pressure sores, the use of triple layer membranes has been shown to decrease the incidence of infections. Their protective properties create a safer healing environment, allowing the body to focus on regeneration without the added stress of battling infection.
3. Enhanced Patient Comfort and Outcomes
Beyond their biological functions, triple layer membranes also enhance patient comfort and satisfaction. Their design is intended to reduce pain and discomfort associated with wound care.
Reduced Dressing Changes
Traditional dressings often require frequent changes, which can be painful and disruptive. Triple-layer membranes, with their superior protection and moisture management, can often remain in place longer. This reduces the need for frequent dressing changes, enhancing patient comfort and reducing the risk of trauma to the wound.
Improved Aesthetics
The ability of triple layer membranes to promote organized tissue growth helps minimize scarring and improve the aesthetic outcomes of healing wounds. Patients can feel more confident about their healing progress, leading to better psychological and emotional well-being during recovery.
Clinical Application:
In cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries, where appearance is paramount, triple-layer membranes have been instrumental in achieving optimal aesthetic results. Their role in minimizing scarring while promoting rapid healing significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
4. Versatility in Clinical Applications
The versatility of triple layer membranes makes them applicable across various medical fields. Their ability to enhance healing and minimize infection risks has made them invaluable in:
- Orthopedic Surgery: Supporting healing in fractures and ligament repairs.
- Dermatology: Managing chronic wounds and improving recovery from skin grafts.
- Ophthalmology: Treating corneal injuries and promoting healing post-surgery.
- Plastic Surgery: Enhancing recovery and minimizing scarring in cosmetic procedures.
Clinical Application:
In orthopedic procedures, for example, triple layer membranes can support the healing of complex fractures by providing structural support while also promoting tissue regeneration. This multifaceted approach significantly enhances recovery and helps prevent complications.
5. Biocompatibility and Safety
Safety and biocompatibility are paramount in any medical treatment. Triple-layer membranes are engineered to integrate seamlessly with the body’s tissues, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Biodegradable Options
Many triple layer membranes are designed to be biodegradable, allowing them to be absorbed by the body over time. This eliminates the need for surgical removal and reduces the overall burden on patients.
Safe Materials
The materials used in triple layer membranes are typically chosen for their safety and compatibility with human tissues. This ensures that patients experience minimal irritation or adverse effects during the healing process.
Clinical Application:
In cases of skin grafting or reconstructive surgeries, the use of biocompatible triple-layer membranes has been beneficial in providing effective support for healing while reducing the risk of complications related to foreign material rejection.
Conclusion
Triple-layer membranes represent a significant advancement in the field of tissue repair and wound healing. By combining protective, bioactive, and scaffold layers, these membranes effectively accelerate healing processes and minimize the risk of infections. Their versatility, enhanced patient comfort, and biocompatibility make them an invaluable tool in modern healthcare.
As medical technology continues to evolve, the application of triple layer membranes is likely to expand, offering innovative solutions to support healing and improve patient outcomes across various medical fields. For healthcare professionals seeking effective strategies to enhance recovery, triple-layer membranes are a promising solution that combines safety, efficacy, and patient satisfaction.